
Sebamed Hairloss
Do you have HAIRLOSS?
WHY DOES HAIRLOSS OCCUR?
WHY DOES HAIRLOSS OCCUR?
Hairloss occurs when the immune system attacks hair follicles, where hair growth begins. It usually starts with one or more small, round, smooth bald patches on the scalp and can progress to total scalp hairloss or complete body hairloss. Reasons for hairloss can range from the simple nutrition deficiency to the more complex health conditions. Anything that interferes with the normal hair growth cycle like medication, illness, infection or chemicals have the capability to stop hair from being formed properly. The common types of hairloss includes male-pattern hairloss, female-pattern hairloss, alopecia areata and thinning of hair known as telogen effluvium.
REASONS FOR HAIRLOSS IN MALES
Male pattern hair loss can be caused by a combination of genetic and hormonal factors. A hormone called dihydrotestosterone (DHT) (produced locally at the site of hair roots) causes a change in the hair roots on the scalp. The hair produced by the affected follicles become progressively smaller in diameter, shorter in length and lighter in color until eventually the follicles shrink completely and stop producing hair.5 Other causes include family history, medications like steroids, thyroid conditions.
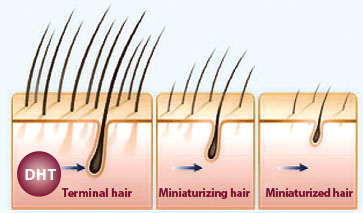
REASONS FOR HAIRLOSS IN FEMALES
There are many causes of hairloss. A combination of genetic and hormonal factors can lead to hairloss. Hair becomes progressively smaller in diameter, shorter in length and lighter in color until eventually the hair roots shrink completely and stop producing hair.
OTHER CAUSES INCLUDE
Hormonal imbalance normally occurs in polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS). Acne, increased facial hair, irregular periods and infertility are all signs of PCOS. Medications used for cancer, arthritis, depression, heart problems, high blood pressure and birth control, excessive intake of vitamin A, protein deficiency, radiation therapy to the head, a trigger event (after a physical or emotional shock), other trigger events include sudden or excessive weight loss, high fever, surgery or a death in the family.
FOOD FOR HEALTHY HAIR

VITAMINS, MINERALS AND IRON
Vitamin C is particularly beneficial for increasing blood circulation on the scalp and supporting the tiny blood vessels that feed the hair roots. E.g. Oranges, limes, lemons, grapefruit, pepper, broccoli, sweet potatoes, kiwi, sprouts. Iron helps make red blood cells, which carry oxygen around the body. Without sufficient oxygen, the hair bulb may not be able to create new hair cells, therefore slowing the hair growth. Iron-rich foods include red meat, nuts, beans, dried fruit, dark leafy vegetables like spinach.
USE A MEDICATED ANTI-HAIRLOSS SHAMPOO

References:
- http://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/hair-loss/tc/hair-loss-what-happens
- http://www.health.com/health/gallery/0,,20727114,00.html
- http://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/hair-loss/features/womenhair-loss-causes#1
- http://www.nhs.uk/conditions/hair-loss/Pages/Introduction.aspx
- http://www.bad.org.uk/shared/get-file.ashx?id=3830&itemtype=document
- http://www.healthline.com/health/male-pattern-baldness
- http://www.bad.org.uk/forthe-public/patient-information-leaflets/hair-loss---female-pattern/?showmore=1&returnlink=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.bad.org.uk%2Ffor-the-public%2Fpatient-informationleaflets#.WMz7xW-GPIV
- http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hair-loss/basics/causes/con-20027666
- http://www.nutritionist-resource.org.uk/articles/healthy-hair.html
- Sebamed manual. Data on file. USV.
DISCLAIMER: This scientific input has been developed & designed by ARAMUC WORLDWIDE [P] LTD. with an educational grant from USV Private Limited. Although great care has been taken in compiling and checking the information, the authors, ARAMUC WORLDWIDE [P] LTD. and its associates or agents, and sponsors shall not be responsible, or in anyway liable for any errors, omissions or inaccuracies in this publication whether arising from negligence or otherwise, however, or for any consequences arising therefrom.




